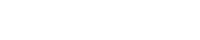Cybersecurity & ChatGPT - Part 1 - A Gentle Introduction
 Photo from Pixabay
Photo from Pixabay
In the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity, staying ahead of emerging threats is a constant challenge. With the advent of Large Language Models (LLMs) and cutting-edge Natural Language Processing (NLP) technologies, a new frontier in cybersecurity has emerged [1]. Since the release of ChatGPT in late 2022, Artificial Intelligence (AI) has impacted society like never before due to the democratization of the AI thought ease-to-use chat-bot interfaces. For the first time, AI reach the general public, revolutionizing how people perceive these technologies. These powerful language models are transforming the way security professionals detect, analyze, and respond to cyber threats. In this first blog post of the series Cybersecurity & ChatGPT, we explore the keys for understanding the foundations of Generative AI technologies like ChatGPT, the principal use cases of LLMs in cybersecurity, and the risks associated to these technologies.
Generative AI: The AI's Creative Genius
Before getting into the subject, we need to define what Generative AI is and how it differs from the classical Machine Learning (ML) models we know. Generative AI or GenAI refers to a class of AI systems that have the ability to generate new content, such as images, text or audio. These systems are designed to understand patterns and structures within existing data and use that knowledge to create new, similar content. One prominent example of Generative AI is Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), where a generator and a discriminator are trained in tandem. The generator creates content, and the discriminator evaluates its authenticity. Through iterative training, the generator becomes increasingly skilled at producing realistic content. Another type of Generative AI is LLMs, such as GPT-4 or PaLM-2. These models can generate coherent and original human-like text from a particular domain by predicting the next word or sequence of words in a given context. They excel in natural language understanding and generation tasks, enabling applications like text completion, translation, summarization, and even creative writing. The versatility of LLMs makes them powerful tools across various domains, from customer service chat-bots to content creation and beyond.
Understanding Large Language Models (LLMs)
Large Language Models, such as GPT by OpenAI or Gemini by Google, represent a groundbreaking advancement in NLP and AI. These models are Deep Neural Networks (typically consisting of tens or hundreds of billions of parameters) trained with massive amounts of public text-based data from the internet (blogs, news, papers, books, etc.). The architecture, based on Transformer models [19], enables them to understand and generate human-like text with remarkable fluency and context awareness.
Large Language Models like GPT-3.5 can be considered a form of unsupervised pre-training for sequence to sequence (seq2seq) tasks. LLMs are trained to predict the next sequence of words from a given input sequence. During pre-training, the model learns to predict the next word in a sequence based on the context of the preceding words. The self-attention mechanism allows the model to weigh the importance of different words in a sequence, allowing the model to focus more on relevant parts of the input sequence. This helps the model to capture contextual relationships and dependencies in the input data to generate best responses. The following figure illustrates the fundamental architecture of a seq2seq model.
LLMs have impressive performance in translation, summarization or question-answering tasks, but the applications of these GenAI models extend beyond language-related uses. They have become instrumental in various industries, including healthcare, finance, and technology, by facilitating automation, improving customer service, and aiding decision-making processes.
ChatGPT for Cybersecurity
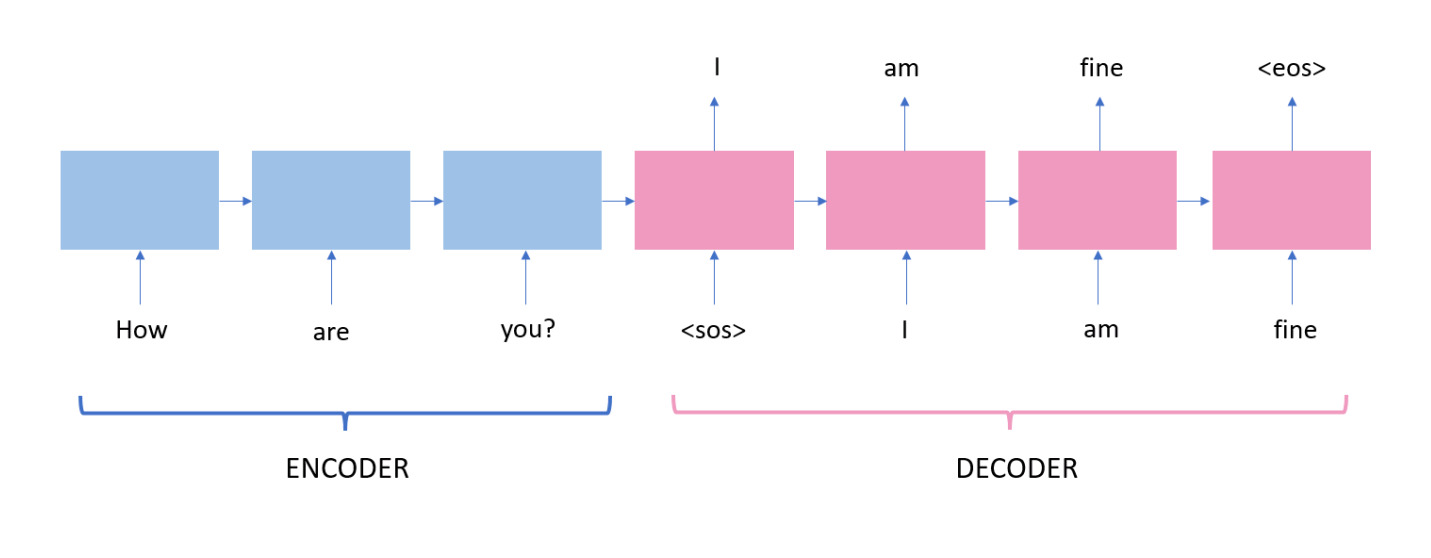
ChatGPT can assist in both offensive and cyber-defense operations. The natural language processing capabilities of ChatGPT and contextual understanding allow LLMs to support cybersecurity teams in many activities:
1) Cyber Threat Intelligence:
ChatGPT can assist cybersecurity analysts in parsing and summarizing vast amounts of textual threat intelligence data, such as open-source intelligence feeds, forums, and news articles, to identify emerging threats and trends. The model can assist in contextualizing and summarizing large volumes of information, helping analysts quickly grasp the significance of specific incidents. Additionally, LLMs can be utilized for natural language understanding, helping to extract relevant information from diverse sources and facilitating the creation of structured threat intelligence reports [6]. ChatGPT can provide insights into emerging threats, vulnerabilities, and attack patterns by analyzing and summarizing information from diverse sources [11].
2) Incident Response:
ChatGPT can aid in the initial triage of security incidents by understanding and processing natural language descriptions of events [13] and forensic artifacts [12]. It can help responders quickly assess the severity of incidents and suggest initial response actions based on historical data and best practices. ChatGPT can assist in identifying potential threats by analyzing patterns and anomalies in real-time. Additionally, it can help responders by providing up-to-date information on known vulnerabilities, attack techniques, and mitigation strategies. Its ability to understand and respond to queries in natural language allows for streamlined communication between security teams, facilitating collaboration and quick decision-making during an incident.
3) Log Analysis and Anomaly Detection:
ChatGPT can assist security analysts by parsing and interpreting complex logs, providing human-readable summaries of events, and extracting relevant information [5]. It can help security teams to analyze structured and unstructured data in many formats (TXT, XML, CSV), providing contextual explanations and insights [16]. ChatGPT can also recognize unusual or suspicious activities by learning normal behavior from historical logs and flagging deviations that may indicate potential security threats [17].
4) Automated Threat Hunting:
ChatGPT can support automated threat hunting by processing natural language queries related to specific threats or IoCs (Indicators of Compromise). It can convert a few plain-text instructions into VQL, SIGMA, REGEX or YARA rules [3] or write SIEM queries (Splunk, Azure Sentinel, ELK) to enhance the capabilities and response times of the Threat Hunting teams. By leveraging ChatGPT's natural language understanding capabilities, threat hunters can use the model to filter and prioritize EDR/XDR alerts [4], streamlining their investigative processes. Additionally, ChatGPT can aid in the creation of playbooks and automated response procedures by generating descriptive and context-aware responses to specific threats.
5) Offensive Security:
ChatGPT is a powerful tool to perform cybersecurity assessments. Red teams use LLMs for:
- Simulate social engineering attacks and enhance Phishing campaigns [14] by generating realistic emails or messages.
- Design penetration testing exercises [10,15] to simulate and identify potential vulnerabilities in computer systems, networks, or applications. ChatGPT can help in creating attack scenarios, crafting payloads, and providing guidance on exploiting vulnerabilities.
- Learn and streamline the use of hacking tools.
- Automated Hacking.
- Attack Payload Generation.
- Realistic URL generation and password guessing with Generative AI (p.e. PassGAN [18]).
6) Security Training & Policy Compliance:
ChatGPT can be used to develop interactive and engaging security awareness training programs. It can simulate phishing attacks, answer security-related queries, and provide real-time guidance on security best practices for users. Also, ChatGPT can help users understand and adhere to security policies [13] by providing explanations and clarifications in natural language.
ChatGPT Constraints and Future Trends in Cybersecurity
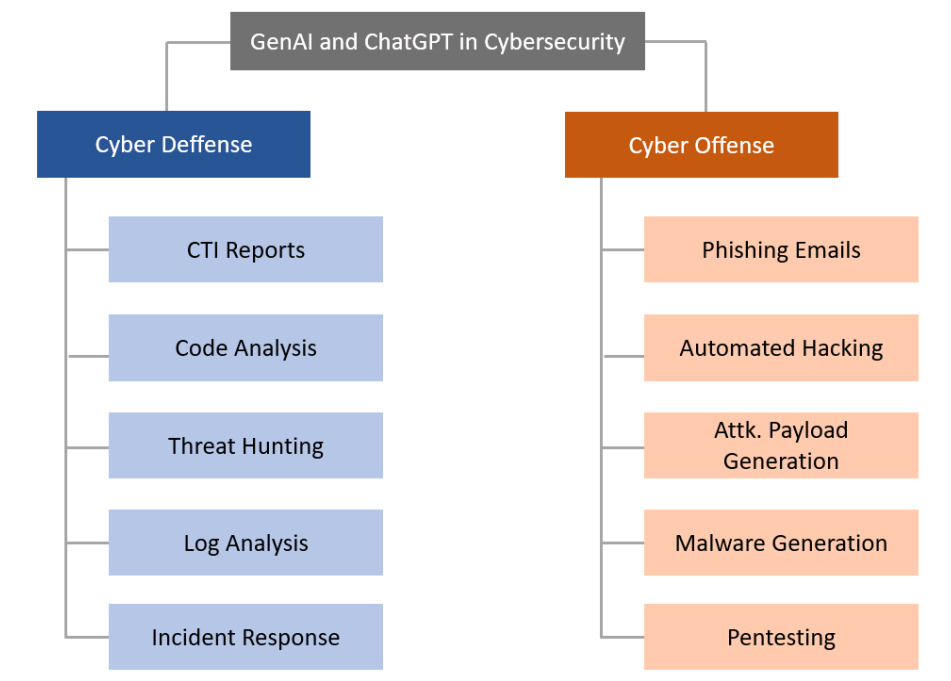
The integration of ChatGPT into cybersecurity represents a promising but challenging journey. Data privacy, hallucinations of the models, perpetuation of biases or lack of transparency are some of the primary constraints of LLMs. Understanding the reasoning behind the model's decisions is crucial for building trust and ensuring the reliability of its outputs in a cybersecurity context. Developing methods to explain and interpret the model's decision-making processes is imperative for effective collaboration between human analysts and AI systems. In a future post, we will cover the main LLMs limitations and constraints for its application in cybersecurity and countermeasures we can implement to solve these challenges.
In conclusion, while there are formidable challenges on the long road ahead in integrating ChatGPT into cybersecurity, the potential benefits make the journey worthwhile. Continued research and development, collaboration between experts in AI and cybersecurity, and a commitment to addressing ethical considerations are essential for realizing the full potential of ChatGPT in safeguarding digital environments.
In the next post of the series, we will dig into the use of ChatGPT and other GenAI tools for Blue Teams, so stay tuned and keep an eye on our latest news!!
- Cybersecurity & ChatGPT - Part 1 - A Gentle Introduction 👈🏼
Hope you enjoy this content!
Stay Tuned and contact us if you have any comment or question!
References:
- [2] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-zUOsO6i92I - SANS
- [5] https://github.com/t0fum4n/OpenAILogParser - OpenAILogParser
- [10] https://github.com/aress31/burpgpt - BurpGPT
- [11] https://socradar.io/chatgpt-for-cti-professionals/ - Socradar
- [12] https://www.mandiant.com/resources/blog/mandiant-leveraging-ai - Mandiant
- [15] https://github.com/ZacharyZcR/SecGPT - SecGPT
- [18] https://github.com/brannondorsey/PassGAN - PassGAN
Follow us: Twitter: @ds4n6_io - Youtube